What Are You Looking For?
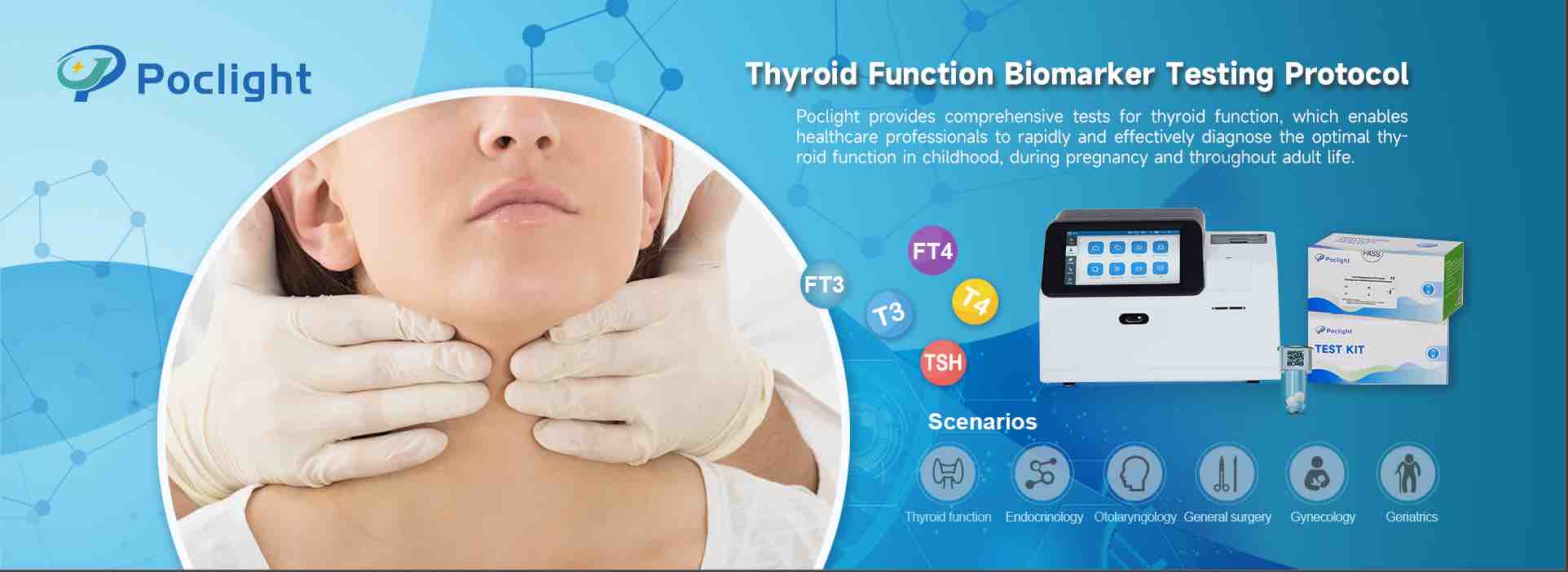
POCT immunoassay system quantitative analyzer
IVD immunoassay system quantitative analyzer
In Vitro Quantitative Test of vet analyzer
SARS-CoV-2 Ag Self-test Kit
Home use COIVD-19 Rapid Test Kit
SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test
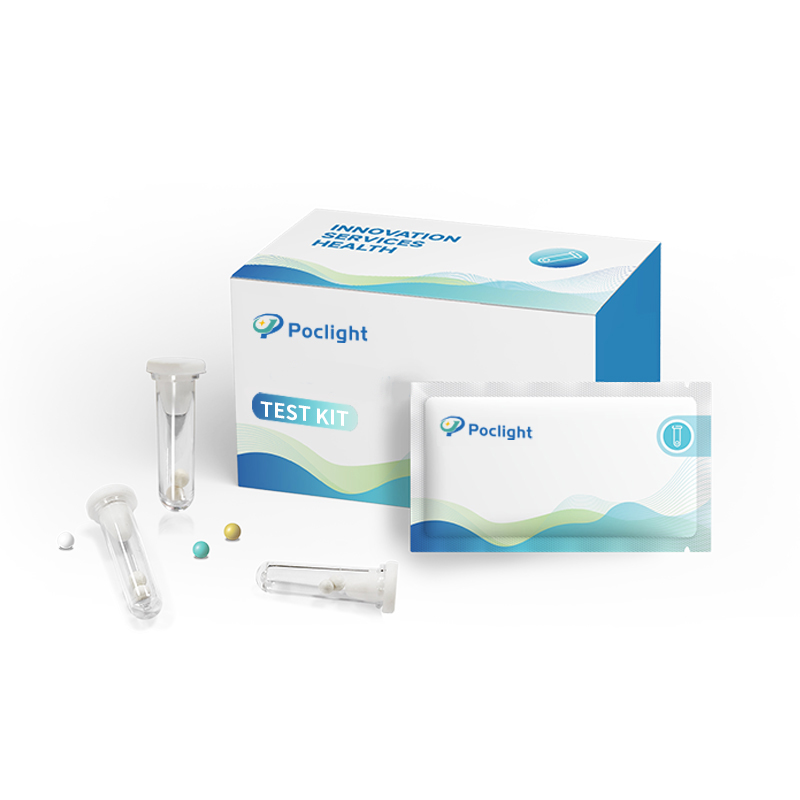
human CRP detection rapid test Reagent
C-Reactive Protein Rapid Test
CRP lyophilized ball reagent test kit

 English
English français
français русский
русский español
español português
português العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Türkçe
Türkçe हिंदी
हिंदी Indonesia
Indonesia 









 IPv6 network supported |
IPv6 network supported | 