1. What It Is
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase protein mainly produced by the liver into the blood in response to inflammation. CRP levels rise rapidly following inflammatory stimuli and decline promptly once the trigger resolves, making it a valuable tool for early diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
|
Parameter
|
C-reactive protein (CRP)
|
|
Primary Site of Production
|
Liver
|
|
Clinical Utility
|
● Monitor inflammation and guide patient management
● Differentiate bacterial from viral infections: CRP level ≥ 50 mg/L are linked to bacterial infections in ~ 90% of cases
|
|
CRP Response & Half-life
|
● Onset of increase: 6–8 hours
● Peak: 24–48 hours
● Half-life: ~19 hours
|
2. Why It Matters
(1) Reliable biomarker: Clinically validated indicator of systemic inflammation, infection, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular risk.
(2) Actionable insights: Supports differential diagnosis (bacterial vs viral), informs antibiotic prescribing, and monitors disease activity to guide treatment.
(3) POC advantage: Rapid, on-site testing enables timely clinical decisions in primary care, emergency, and bedside settings.
3. Reference Ranges:
|
Item
|
Result
|
Interpretation
|
|
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein
(hs-CRP Assay Kit)
(assessing risk of cardiovascular events)
|
1 mg/L
|
Low cardiovascular risk
|
|
1–3 mg/L
|
Moderate cardiovascular risk; anti-inflammatory therapy recommended
|
|
≥ 3 mg/L
|
High cardiovascular risk; anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic therapy recommended
|
|
C-Reactive Protein (CRP Test Kit)
|
< 10 mg/L
|
Normal
|
|
> 10 mg/L
|
Indicates inflammation; possible infection, autoimmune disease, or chronic inflammation
|
|
> 50 mg/L
|
Indicates bacterial infection (~90%); viral infection uncommon
|
|
> 100 mg/L
|
Severe elevation, generally seen in acute bacterial infections
|
Note: Results should be interpreted in the context of the patient’s clinical condition. Laboratories are recommended to establish population-specific reference values for their region, as the levels may vary with demographic and methodological factors.
4. When and Where to Measure CRP
|
Clinical Setting
|
When / Indication
|
Purpose / Clinical Use
|
|
Primary care / Outpatient clinics
|
At onset of acute symptoms; routine follow-up for chronic inflammation
|
Rapid assessment of infection; guide antibiotic use; monitor autoimmune disease activity
|
|
Emergency department / Urgent care
|
Suspected acute infection, fever, or trauma
|
Triage patients; monitor acute inflammation and treatment response
|
|
Hospital / Laboratory / ICU
|
Post-surgery, trauma, sepsis, or during treatment
|
Assess inflammation; monitor therapy effectiveness, and track disease progression
|

5. Why Poclight CRP Stands Out: Facts & Features
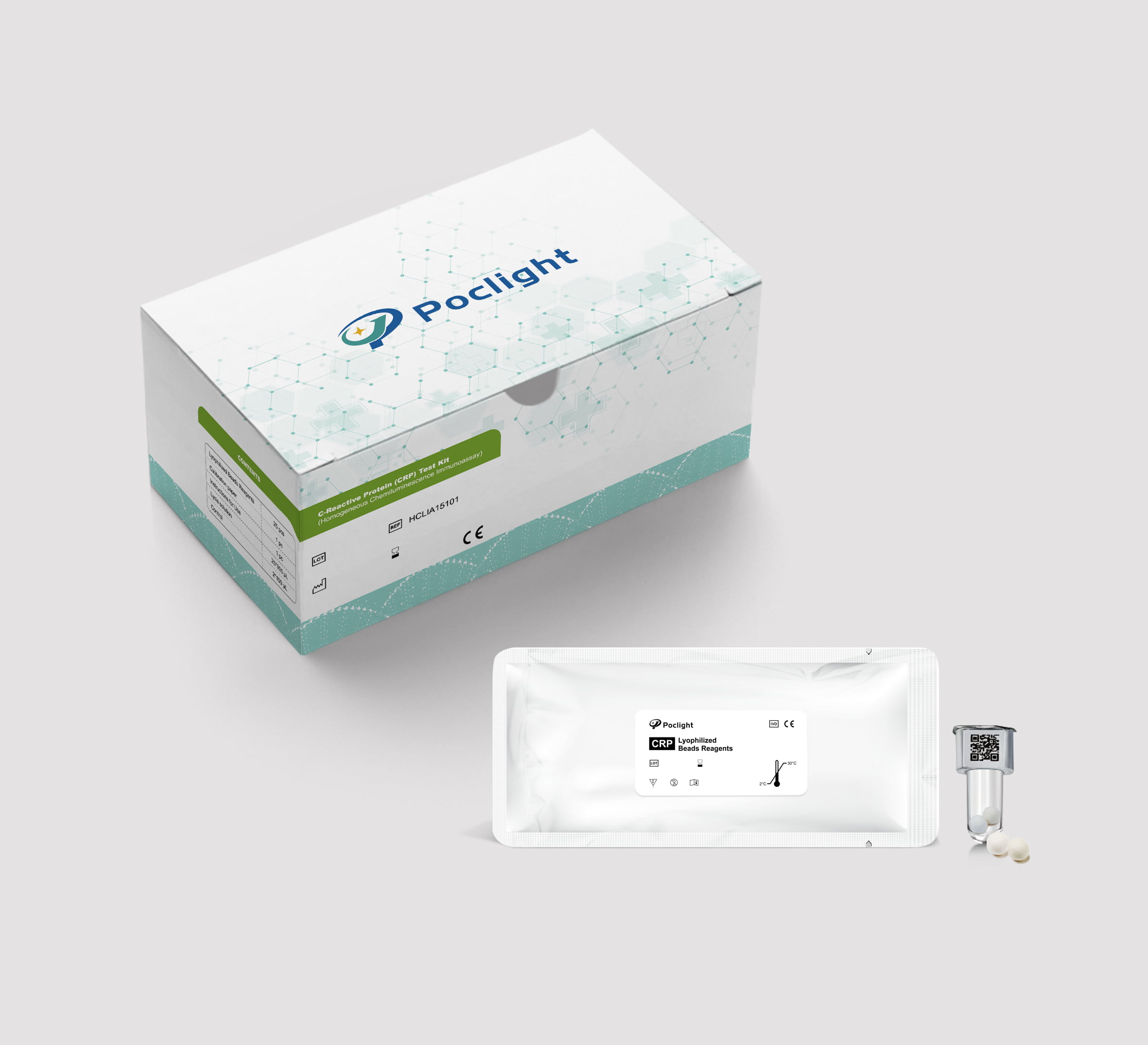
(1) Assay Specifications
|
Item
|
Specification / Value
|
|
Detection Limit (LOD)
|
≤ 0.5 mg/L
|
|
Measurement Range
|
0.5 - 320 mg/L
within this linear range, the linear correlation coefficient r should be not less than 0.990
|
|
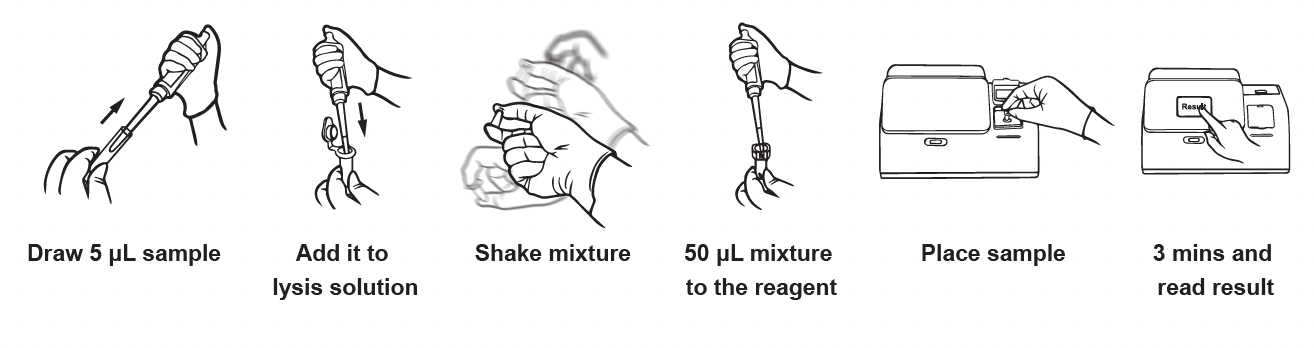
Sample Volume
|
5 μL
|
|
Sample Type
|
Serum, Plasma, Whole Blood
|
|
Assay Time / Turnaround
|
3 min
|
|
Precision (CV%)
|
5%
|
|
Reference Range
|
<10 mg/L
|
(2) Key Features:
a. Advanced patent technology: 5th generation homogenous CLIA, CRET technology
b. Compatible with Poclight C5000 analyzer: Designed for POC settings, auto-calibration, built-in scanner, internal mixing component, and more

c. Individually packaged: on-demand testing
d. Room-temperature transport, no cold chain required: saves logistic costs
e. Lyophilized reagents: freeze-dried reagent for room temperature storage (2–30°C) with extended shelf life of 18 months
f. Operational efficiency: intuitive process, reduced workload, and optimal lab performance

 English
English français
français русский
русский español
español português
português العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Türkçe
Türkçe हिंदी
हिंदी Indonesia
Indonesia 











 IPv6 network supported |
IPv6 network supported | 