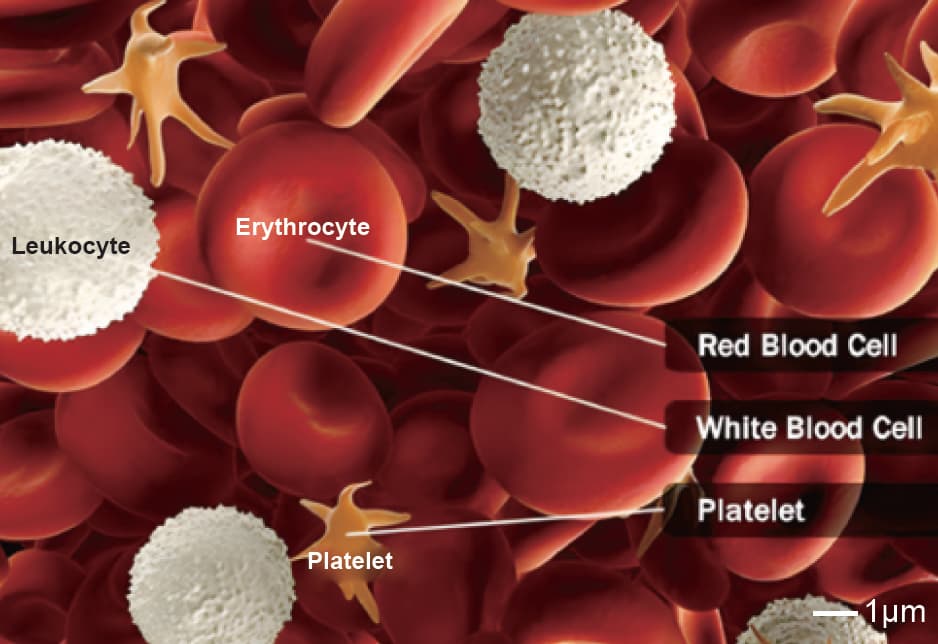
1.What is Platelet?
Platelets, fragments of cytoplasm derived from bone marrow megakaryocytes, play a central role in hemostasis and thrombosis. When blood vessels are injured, platelets adhere, activate, and aggregate to stop bleeding. Abnormal platelet function can lead to bleeding disorders or thrombotic events. With the widespread use of antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin and clopidogrel, precise assessment of platelet activation function is increasingly important. Poclight’s next-generation Homogeneous CLIA (Chemiluminescence Immunoassay) technology brings a new level of accuracy and speed to platelet function testing.
.
2. Platelet Function and Clinical Significance
Platelet-mediated hemostasis involves three key steps:
a. Adhesion
When the endothelium is disrupted, platelets adhere to the vessel wall via von Willebrand Factor (VWF) and collagen. This process is mediated by glycoprotein receptors CD42a/b/d (GPIb-IX-V), a critical step in platelet adhesion.
b. Activation
Platelets are activated through G-protein-coupled receptors binding to ligands such as thrombin, ADP, ATP, and prostanoids. Activated platelets change shape to a dendritic or octopus-like form.
c. Aggregation
Activated platelets are interconnected by fibrinogen and receptors CD41/61 (GPIIb/IIIa). Platelet granules release their contents into the extracellular fluid, among which CD62P (P-selectin) promotes platelet aggregation through platelet–platelet and platelet–fibrin interactions.
Platelet function
Hemostasis and thrombosis: The Key Role of Platelets
Physiological function: The biological behavior and function of platelets are extremely complex. This includes participating in hemostasis and coagulation, maintaining vascular function, regulating inflammation, the body's immune defense, wound healing, tumor growth and metastasis, etc. Therefore, in clinical activities, the monitoring of platelet functionality is receiving increasing attention.
The average lifespan of platelets is 7 to 9 days. Senescent and dead platelets are eventually phagocytosed and processed in the spleen through the bloodstream.
Clinical Significance
- Thrombosis Risk Assessment: Patients with hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular conditions, as well as those on antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy.
- Pre/Postoperative Evaluation: Predicting thrombus formation and guiding prophylactic measures.
- Platelet Dysfunction Disorders: For example, Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia (CD41/61 deficiency) and Bernard-Soulier syndrome (CD42a/b/d deficiency).
- Antiplatelet Therapy Monitoring: Supporting decisions for drugs like clopidogrel, ticagrelor, and prasugrel.
- Various detection functions:
| Defect of platelet momoprotein receptor |
CD61(GP IIIa)
|
CD(GP IIb)
|
CD42a(GP I X)
|
CD42b(GP I b)
|
|
Platelet Activation
|
CD62P(P
selectin)
|
CD61(GP IIIa)
|
CD61
Antibody(PAC-1)
|
CD45(White blood cell platelet aggregation)
|
|
Platelet Function
|
AA-CD62P
|
ADP-CD62P
|
…
|
3. Advantages of Poclight Platelet Activation Function Test
|
Feature
|
Description
|
|
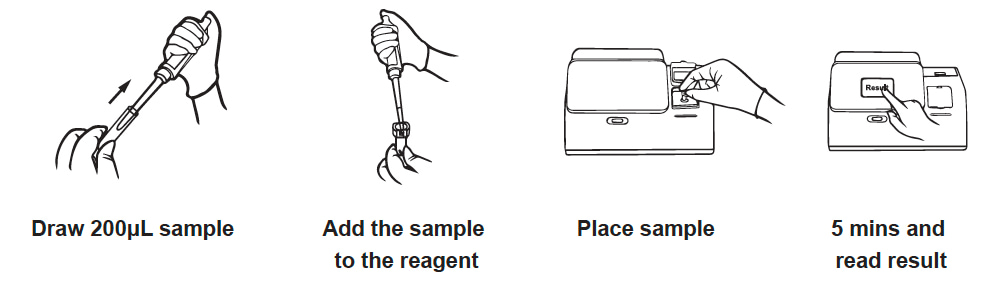
Accurate & Fast
|
Quantitative results in just 5 minutes, enabling rapid clinical decisions.
|
|
Portable & Minimalist
|
One-step sample addition, maintenance-free, suitable for point-of-care testing.
|
|
True & Reliable
|
Technical details to be provided by the team to support this claim.
|
|
Quality Assurance
|
Supports quality control products and continuous QC checks, ensuring reliable results.
|
Technical Highlights:
Employs Homogeneous CLIA technology to detect multiple platelet surface markers (CD41, CD42, CD61, CD62P) for comprehensive assessment.
Evaluates the full spectrum of platelet function—adhesion, activation, and aggregation—delivering more comprehensive and physiologically-relevant results.
4. Compatible Devices
The Poclight Platelet Activation Function Test is fully compatible with Poclight latest C5000 Analyzer, offering seamless integration into clinical and point-of-care settings. Key compatibility features include:
- Plug-and-Play Operation: Simple one-step sample addition for immediate testing.
- Portable Analyzer Integration: Works with compact, maintenance-free devices suitable for outpatient clinics or bedside monitoring.
- Future Expansion: Designed to support upcoming analyzer models based on the Homogeneous CLIA platform.
- Note: For detailed technical specifications and compatibility with your laboratory instruments, please contact our technical support team at overseas@poclight.com.

5. Clinical Applications
- Outpatient Thrombosis Risk Screening: Quickly assess high-risk patients and guide antiplatelet therapy.
- Pre/Postoperative Monitoring: Track platelet activity changes to optimize surgical management.
- Antiplatelet Drug Efficacy Evaluation: Support individualized medication decisions and reduce bleeding or thrombotic events.
- Diagnosis of Platelet Dysfunction Disorders: Provide molecular-level insights for rare platelet diseases.
6. Influencing factors
- Genetic factors: Genes determine each person's basic platelet activity and their response to drugs.
- Drugs: Antiplatelet drugs, NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen), certain antibiotics, antidepressants, etc., can all affect their function.
- Disease status: Chronic diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease, and autoimmune diseases are often accompanied by high platelet reactivity (easier to form blood clots).
- Lifestyle:
Diet: Omega-3 fatty acids, garlic, ginger, and certain vitamins (such as VC and VE) may inhibit platelet function.
Smoking and drinking: Smoking activates platelets, while moderate drinking may inhibit them.
Physiological conditions: Stress, exercise, and aging can all increase platelet activity.
7. Future Outlook
Platelet activation function testing is evolving towards speed, portability, standardization, and intelligence. Poclight’s Homogeneous CLIA platform not only shortens testing time but also delivers reliable, high-quality data, supporting precise assessment of bleeding and thrombotic risk. With ongoing technological innovation, this approach will play an increasingly vital role in precision medicine and individualized patient care.
8. Chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer(CRET)
Detection principle:
CRET cell technique utilizes the molecules on the platelet membrane to specifically fix and bind to the corresponding antibody 1-labeled DNA1, antibody 2-labeled DNA2, and AE-labeled DNA3 to form complexes. By detecting the light intensity via CRET, the expression levels of various antigens and receptor molecules in the sample can be detected.
| Project |
Reference Interval |
Project |
Reference Interval
|
|
CD62P
|
1.04-4.52%
|
CD42a
|
82.65-100%
|
|
PAC-1 (GPIIb/IIIa)
|
0-10%
|
CD42b
|
81.86-100%
|
|
CD61
|
60-92.13%
|
CD45
|
12.95%-46.04%
|
|
CD41
|
90.7-99.0%
|
|
|
Detection method:
- Nucleic acid technology is integrated into immunodiagnosis, leveraging the proximity effect of nucleic acids.
- The properties of graphene oxide are strategically utilized, eliminating the need for magnetic beads and their associated separation and washing steps, and simplifying the fluidic path.
- The introduction of enzymatic cycling amplification technology enhances detection sensitivity by 1 to 2 orders of magnitude, improving overall performance while simultaneously simplifying the process.
Advantage:
CRET compensates for the drawbacks of flow cytometry and enables:
- Fast, reliable detection in just 5-10 minutes.
- A simple and minimalist operational procedure.
- Low-cost testing with no hidden fees.
- Easy adoption in all levels of hospitals and departments.
- Accurate in vivo status: Not affected by platelet aggregation or in vitro activation issues.
Contact Us
E-mail: overseas@poclight.com

 English
English français
français русский
русский español
español português
português العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Türkçe
Türkçe हिंदी
हिंदी Indonesia
Indonesia 








 IPv6 network supported |
IPv6 network supported | 